Curves
These are 2D shapes that may make up the cross sectional of a surface.
Ellipses
These are shapes such as an oval or circle.
General Form:
and are constants.
Hyperbola
There are two different types of hyperbolas, ones with a vertical asymptote (#Type I )and ones with a horizontal asymptote (#Type II).
Type I
As mentioned before these have a vertical asymptote.
General Form:
Type II
As mentioned before these have a horizontal asymptote.
General Form:
Surfaces
, and are constants.
Ellipsoid
The Cross-sectionals of these shapes are either ellipses or points.
They generally follow the form:
Elliptic Paraboloid
They generally follow the form:
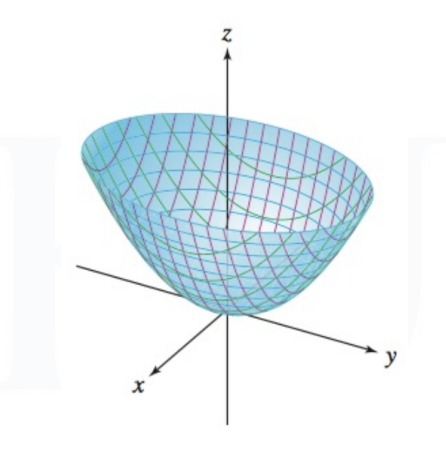
Variables can be swapped the variable that is equal to the other two squared summed will be the direction of the concavity (hollow part of the cup).
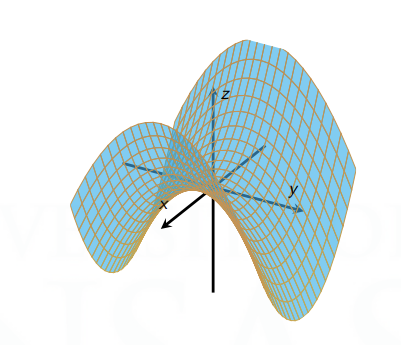
Hyperbolic Paraboloid (Saddle)
They generally follow the form:
Hyperboloid of One Sheet
They generally follow the form:
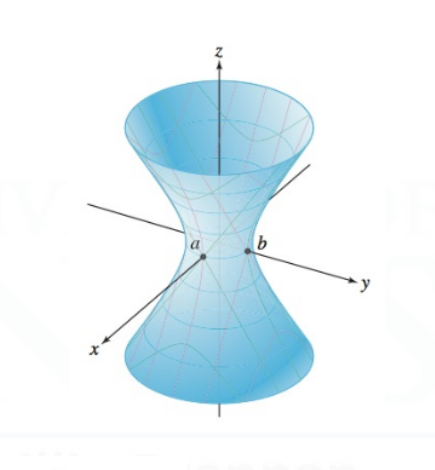
Hyperboloid of Two Sheet
They generally follow the form:
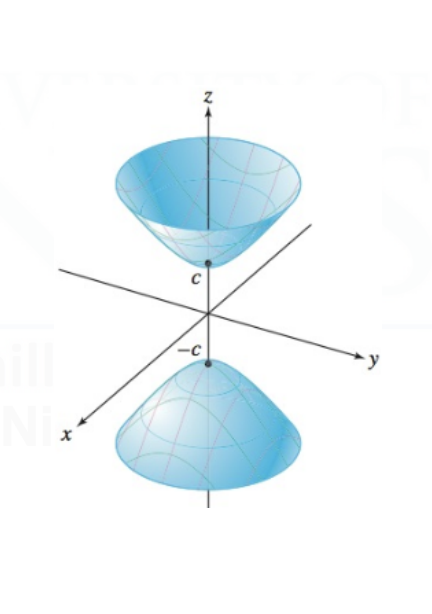
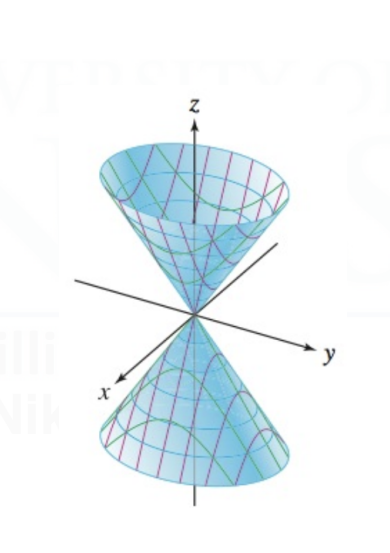
Cone
They generally follow the form: